Librium contained the benzodiazepine derivative chlordiazepoxide (initially called methaminodiazepoxide) which has been used for the treatment of myriad conditions including anxiety, seizures, and insomnia, for more than 60 years now. Chlordiazepoxide produces a calming effect on the brain and nerves, which helps to reduce anxiety symptoms, but also to reduce alcohol withdrawal symptoms, and to promote relaxation for surgery. It has sedative, appetite-stimulating, and weak analgesic action. Discovered in the late 1950s by the Polish American chemist Leo H. Sternbach (1908-2005), chlordiazepoxide is a long-acting benzodiazepine. Chlordiazepoxide is among the most used first line agents in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. It belongs to a large class of psychotropic compounds, including also diazepam (Valium) and many other benzodiazepine tranquilizers (>50), prescribed to treat anxiety, seizures, withdrawal states, insomnia, agitation and for procedural sedation. In the early 1960s, the commercialization of Librium by Hoffmann-La Roche was one of the major revolutions in the pharmacological treatment of anxiety disorders. Today, chlordiazepoxide remains among the most commonly used oral benzodiazepines.






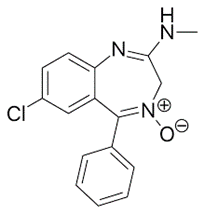
chlordiazepoxide