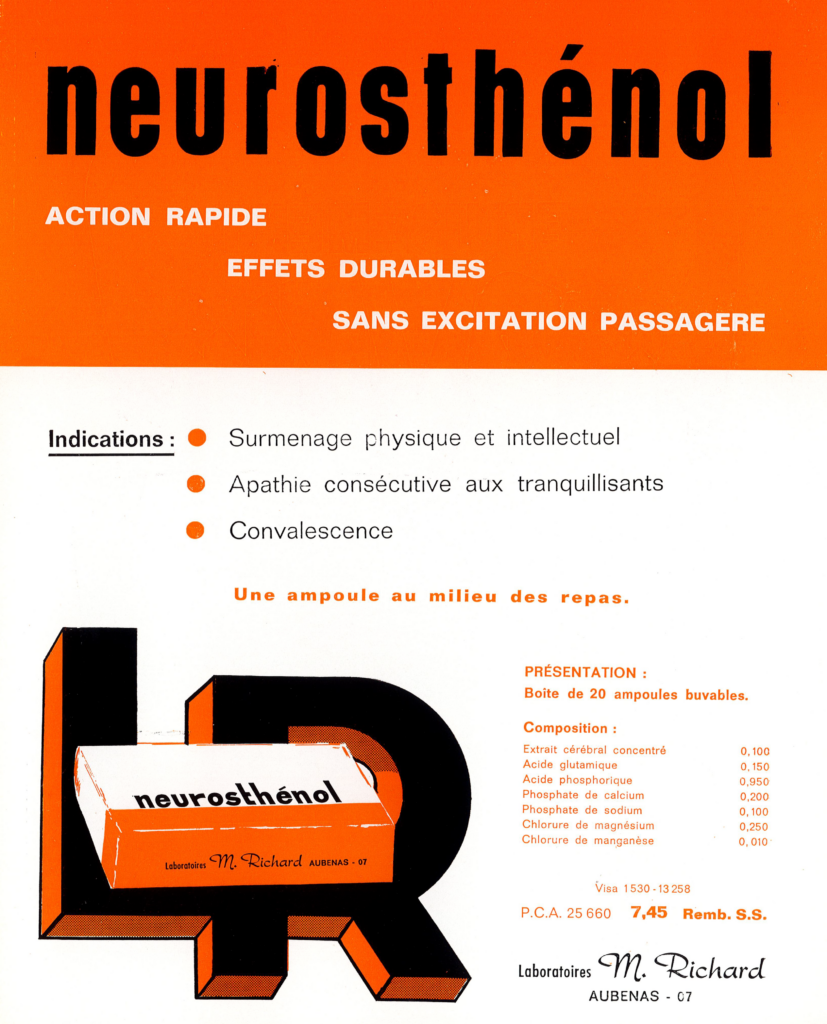
Neurosténol was used to treat temporary asthenia (fatigue), to support people in phase of recovery or those suffering from apathy after a phase of physical or intellectual overwork for example. This liquid product, formulated in drinking ampules, contained a cocktail of active ingredients including glutamic acid, phosphoric acid, calcium and sodium phosphate, magnesium chloride, in addition to a not-well-defined “concentrated cerebral extract”. Glutamic acid (Glu) is an amino acid frequently used to improve metal capacities, often considered as a “brain food” to give a lift from fatigue and to help to take control over mental deficit. Glu is a common neurotransmitter in brain function, acting also as a precursor for the synthesis of Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in GABAergic neurons. The use of an undefined “concentrated cerebral extract” is uncommon. The product likely served as a cognitive enhancer (nootropic agent) used in an attempt to improve memory, increase mental alertness and concentration as well as boost energy levels and wakefulness. This type of undefined brain extract is no longer used today.