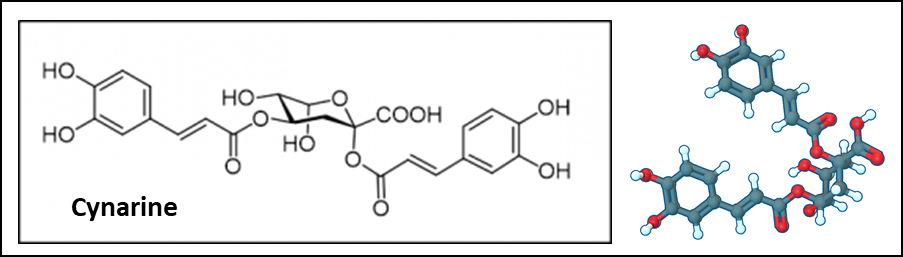
Cynarine (1,3-dicaffeoylquinic acid) is an alkyl caffeate ester obtained by the condensation of hydroxy groups at positions 1 and 3 of quinic acid with two molecules of trans-caffeic acid. Cynarine is a natural product found in several plants, notably in the artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.). The product is known to stimulate digestive secretions and to prevent endothelial inflammation. This natural polyphenolic compound displays also vasorelaxant and anti-swelling effects. It is well-known as a liver protection and lipid lowering agent. Cynarin has been shown to reduce fat deposition and to lower the levels of the enzymes aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) released by liver cells due to excessive lipid accumulation. It is considered a useful product to combat non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Cynarine helps to reduce serum and hepatic cholesterol levels. The drug remains used to day. There are numerous medicinal products derived from artichoke leaf extracts containing cynarine, recommended for the management of functional dyspepsia symptoms (digestive troubles). The advert highlighted the hepatoprotective effects of cynarine (“the smile of the hepatic patient”) and more generally the benefit of the product to treat hepatic and gastrointestinal disorders.