The drug Acidrine® corresponded to an association of nopoxamine lauryl-sulfate, galactane sulfate and aluminium basic amino-acetate, used in the treatment of gastro-duodenal pains. The drug was useful to treat and prevent gastritis or duodenitis (without ulcer); it was considered as an antiacid therapy.


Nopoxamine, also known as myrtecaine, has a muscle relaxant effect. This pinene derivative was useful to treat muscle strains, tendinitis or ligament sprains and joint pain. It was used in combination with other active ingredients in the management of muscle or ligament pains. The role of aluminium amino-acetate was to help reducing gastric secretion of acid and protecting the gastric mucosa. Aluminium salts are known as mucosal protecting antiulcer compounds.
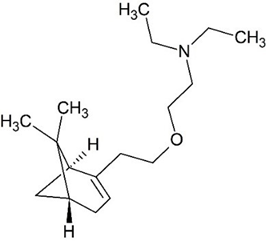
Acidrine is no longer used today but nopoxamine can be found in other medicinal products, notably in a combination product with diethylamine salicylate (Algesal), a topical cream used as a local anaesthetic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory product.
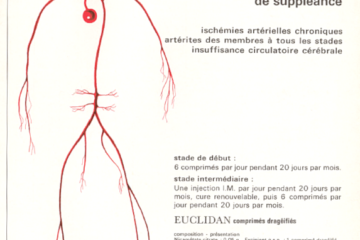
A nice colored illustration of the three main properties of Acidrine: pain relief (analgesia), antispasmodic and antiseptic. The combination of three active principles, schematized with superimposed organs, offered a protection against gastrointestinal injuries