The active ingredient of Glucidoral® tablet was glybutamide, a classical sulfonylurea used as an antidiabetic agent, also known as carbutamide. This oral hypoglycemic drug belongs to a large family of sulphonamide derivatives, initially discovered in Germany in the early 1950s. From the chemical viewpoint, glybutamide is a butyl-sulfonyl-urea, structurally close to another well-known derivative, tolbutamide. First generation sulfonylureas are still occasionally used today for the treatment of mild-to-moderate type 2 diabetes mellitus, for the management of glycaemia (in conjunction with diet). These compounds lower blood sugar as a result of increasing release of insulin from the pancreas. They stimulate insulin release from pancreatic beta cells. As such, they are not effective in type 1 diabetes, in which there is a deficiency in insulin producing pancreatic beta cells. Carbutamide is no longer used today, whereas tolbutamide is still used occasionally. However, there are now more potent sulphonamides, called 2nd generation sulfonylureas, active at lower concentrations than the 1st generation compounds and with fewer side effects (such as headache, nausea, fatigue and alcohol intolerance (flushing)).


Sulfonylureas have been extremely useful for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. However, the long term use of these compounds has been associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular alterations (ventricular arrhythmia) and cancer. This is why alternative medications are often preferred in high-income countries. There are many types of glucose-lowering drugs. However, these affordable sulphonamide compounds remain largely prescribed in low- and middle-income countries.
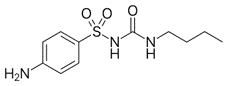
(glybutamide)