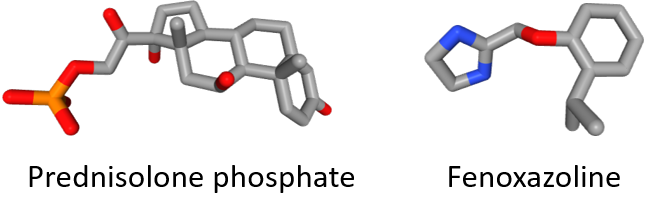
Deturgylone® combined two active substances: (1) the synthetic glucocorticoid prednisolone phosphate which has anti-inflammatory and immunomodulating properties, and (2) the imidazoline derivative fenoxazoline acting as a nasal vasoconstrictor. The drug, delivered via a nasal spray, was used to treat rhinitis, sinusitis, allergies of the ENT (ear, nose and throat) region, or after local ENT surgery.
The use of Deturgylone® was abandoned in the 1980s. The overuse of fenoxazoline as a nasal decongestant was found to induce arterial hypertension, with severe damages reported in some cases (such as digital ischemia and necrosis). However, the active ingredient prednisolone phosphate remains largely used today to treat local inflammation, notably in cases of bacterial keratitis.
In addition, a liposomal formulation of prednisolone phosphate was found to exhibit anticancer properties, reducing tumor growth in murine models and potentiating the anticancer activity of established drugs, like 5-fluorouracil. Tumor-associated inflammation is recognized as an important tumor growth propagator. Therefore, the use of an anti-inflammatory glucocorticoid like prednisolone represents an attractive option to boost a cancer treatment. The design of drug-loaded long-circulating liposomes facilitates accumulation of the active principle at sites of malignancy. The encapsulated compound shows anti-angiogenic and anti-metastatic effects, which can greatly help to avoid or reduce resistance to anticancer drugs. These liposomal forms of prednisolone are now evaluated for the treatment of diverse pathologies, such as arthritis.
Deturgylone was mainly used to threat rhinitis. The illustration referred to the decongesting action of the drug, liberating the noose and facilitating breath. A pictural illustration of the mucosa liberated by the molecule, like an invading, liberating army…